Labral Tears
- Diagnosis
- Non-operative Options
- Operative Options
- Before Your Surgery
- After Your Surgery
- Your Rehab
The shoulder joint is a “ball and socket” joint that enables smooth gliding and thereby the movements of arms. However, it is inherently unstable because of the shallow socket. A soft rim of cartilage, the labrum, lines the socket and deepens it so that it accommodates the head of the upper arm bone better.
Causes of Shoulder Labral Tear
Traumatic injury to the shoulder or overuse of shoulder (throwing, weightlifting) may cause labral tear. In addition, ageing may weaken the labrum leading to injury.
Symptoms of Shoulder Labral Tear
Shoulder labral tear injury may cause symptoms such as:
- Pain
- Catching or locking sensation
- Decreased range of motion
- Joint instability
- Physical Therapy Intro
- Shoulder and Elbow Steroid Injection
Your doctor may start with conservative approaches such as prescribing anti-inflammatory medications and advise rest to relieve symptoms until diagnostic scans are done. Rehabilitation exercises may be recommended to strengthen rotator cuff muscles.
Want to know more?
If the symptoms do not resolve with these conservative measures, your doctor may recommend arthroscopic surgery.
During arthroscopic surgery, your surgeon examines the labrum and the biceps tendon. If the damage is confined to the labrum without involving the tendon, then the torn flap of the labrum will be removed. In cases where the tendon is also involved or if there is detachment of the tendon, absorbable wires or sutures will be used to repair and reattach the tendon.

Once you and your doctor decide that surgery will help you, you will need to learn what to expect from the surgery and how to actively participate in the treatment plan for the best results afterward.
Preparing mentally and physically for surgery is an important step toward a successful result. Understanding the process, and your role in it, will help you recover more quickly and have fewer problems.
Before surgery, your doctor will perform a complete physical examination to make sure you don’t have any conditions that could interfere with the surgery or the outcomes.
- Routine tests, such as blood tests and X-rays may be performed.
- Discuss any medications you are taking with your doctor as you may have to stop or alter your intake before surgery. If you are taking aspirin or anti-inflammatory medications or any drugs that increase the risk of bleeding, you will need to stop taking them one week before surgery to minimize bleeding.
- Discuss with your doctor about preparing for potential blood replacement, medical interventions and other treatments prior to surgery.
- Report any infections to your surgeon. Surgery cannot be performed until all infections have cleared up.
- If you smoke, you should stop or cut down as smoking interferes with wound healing and can affect your recovery.
- Have someone available to take you home, as driving is not recommended for at least 24 hours or as advised.
- You may need help with everyday tasks such as cooking, shopping and laundry.
- Put items that you use often within easy reach, so you won’t have to stretch and bend as often.
- After Surgery Video
- Shoulder Surgery Recovery Video
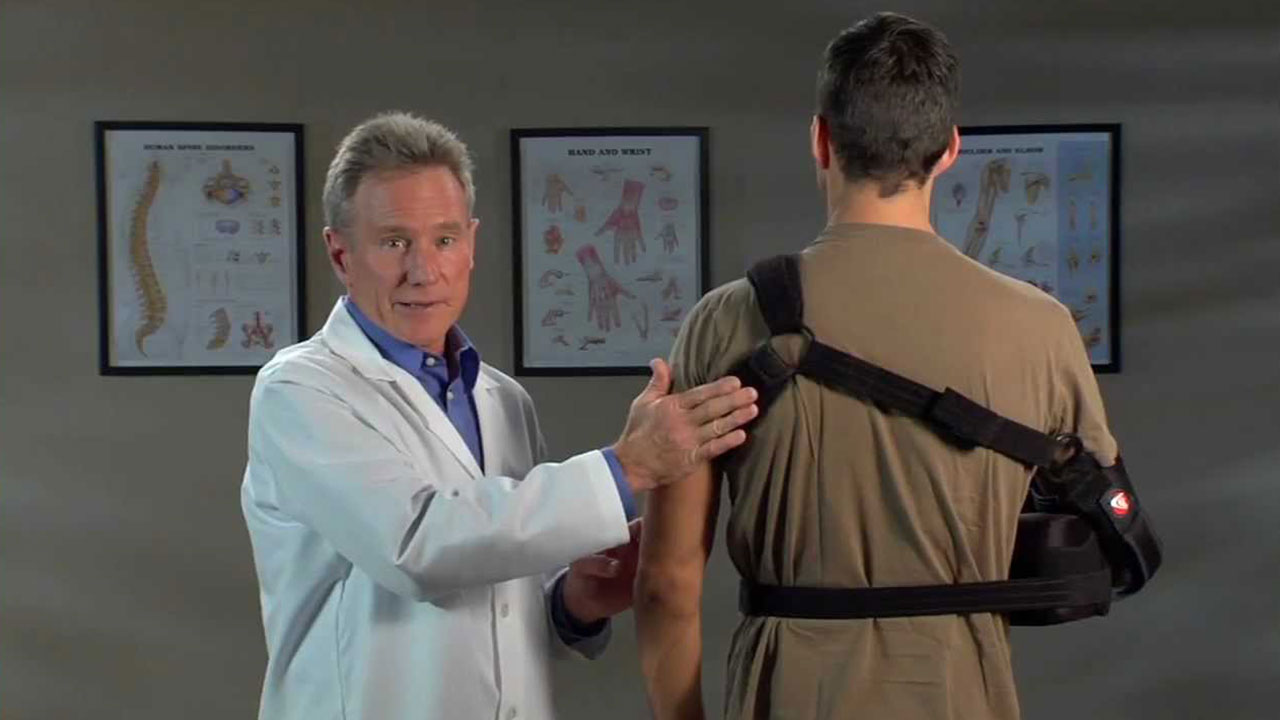
- Post-operative Sling
After the surgery, you will be given a shoulder sling to wear for 3-4 weeks.
Want to know more?
- Physical Therapy Intro Video
- Finger ROM Video
- Standard Elbow ROM Video
- Shoulder ROM Video
You will be advised motion and flexibility exercises after the sling is removed. These exercises increase the range of motion and flexibility of the shoulder joint.